5 Common E-commerce SEO mistakes and how to fix them

SEO for E-commerce websites can be difficult to manage; due to the potential vast array of pages, templates and different content formats.
After working with a range of E-commerce clients, there are particular SEO mistakes that we come across more often than others, which are normally due to default CMS settings which haven’t been tweaked, an inattentive approach to content and/or a lack of general website maintenance.
Discover some of the most common E-commerce SEO mistakes I come across below while making sure you or your clients aren’t making the same mistakes.
Poor Site Speed
Site speed is one of only a few ranking factors confirmed by Google. The content-heavy nature of e-commerce pages; including the likes of high-resolution product images and videos means that page speed can be easily compromised.
As well as being an SEO ranking factor, several studies have indicated that page speeds can have a huge impact in terms of bounce rates, and most importantly, conversion rates.

Google’s new Core Web Vitals report, in Google Search Console, will identify URLs which fit into three potential categories; “Poor”, “Needs Improvement” and “Good” when it comes to user experience metrics.
The Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) metric marks the point in the page load timeline when the page’s main content has fully loaded which should occur before 2.5 seconds to be deemed “good”.

Once you have identified slow URLs, Google’s John Mueller recommends using Webpagetest.org to diagnose what is slowing down the page speed. GT Metrix and Google’s page speed insights tool are also helpful in these situations too.
https://twitter.com/JohnMu/status/1274018453247139841?ref_src=twsrc{8e70974195c48f015656ec00029c2bf559b83ca472845d96d7b604466648386d}5Etfw{8e70974195c48f015656ec00029c2bf559b83ca472845d96d7b604466648386d}7Ctwcamp{8e70974195c48f015656ec00029c2bf559b83ca472845d96d7b604466648386d}5Etweetembed{8e70974195c48f015656ec00029c2bf559b83ca472845d96d7b604466648386d}7Ctwterm{8e70974195c48f015656ec00029c2bf559b83ca472845d96d7b604466648386d}5E1274018453247139841{8e70974195c48f015656ec00029c2bf559b83ca472845d96d7b604466648386d}7Ctwgr{8e70974195c48f015656ec00029c2bf559b83ca472845d96d7b604466648386d}5E&ref_url=https{8e70974195c48f015656ec00029c2bf559b83ca472845d96d7b604466648386d}3A{8e70974195c48f015656ec00029c2bf559b83ca472845d96d7b604466648386d}2F{8e70974195c48f015656ec00029c2bf559b83ca472845d96d7b604466648386d}2Fwww.seroundtable.com{8e70974195c48f015656ec00029c2bf559b83ca472845d96d7b604466648386d}2Fiagnose-largest-contentful-paint-lcp-slowness-29651.html
Faceted Navigation not set up to complement SEO
It’s very common for e-commerce sites to have thousands of pages housed under lots of filters and facets which allow the user to narrow down their options when choosing products.
The nature of faceted navigation means that more often than not, extremely similar content can be present on a number of different URLs which can cause huge problems; with arguably the biggest being that this confuses Google into which of the group of similar pages to rank for specific queries.
Initially, keyword research should be undertaken to determine which facets have the potential to generate organic traffic and these pages should then be optimised and most importantly – unique.
Pages generated via faceted navigation with zero potential search traffic should either be canonicalised to a very similar page (usually to the most related category page without any filters or facets selected) or alternatively “no-indexed”.
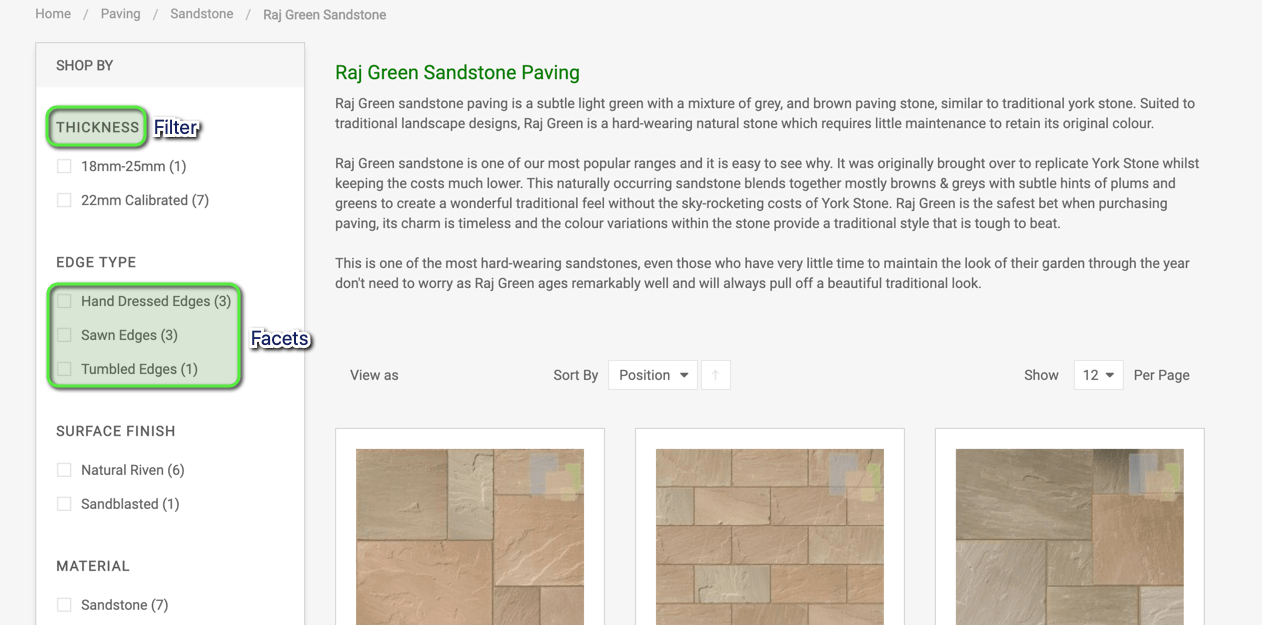
Lack of Category page Content
Category pages are great for ranking for broader keywords with substantial search volume. However, some e-commerce category pages lack the required amount of content that is needed to provide topical relevance to Google.
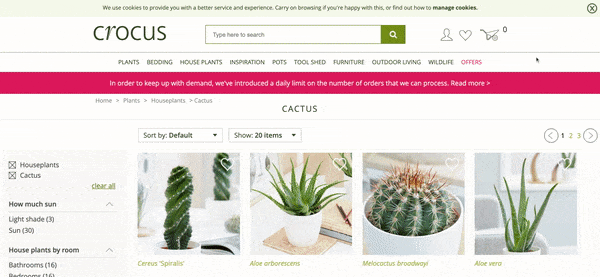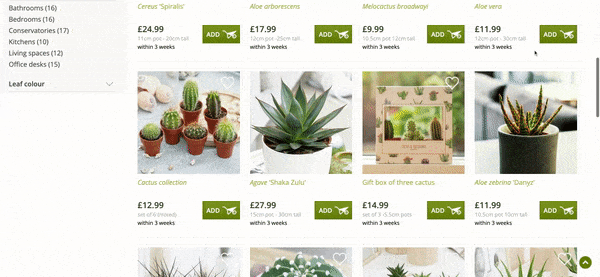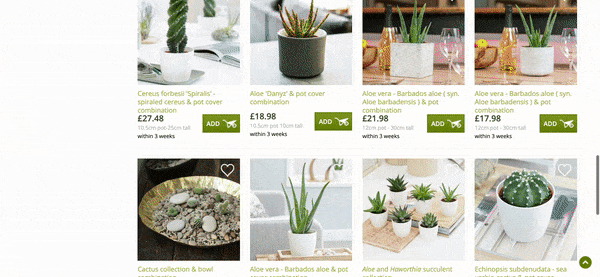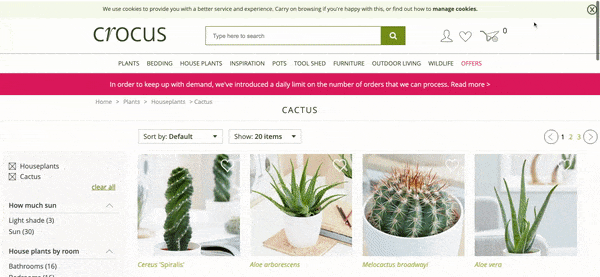
Here is an example:
The query “Cactus Plants” generates around 2,100 UK searches a month.
Crocus.co.uk, a huge website which sells plants, is an example of where their “Cactus Plants” page is lacking content, especially copy, thus also lacking the topical relevance for Google to rank this for related keywords.
The importance of comprehensive content is highlighted in this quote by Google’s John Mueller:
“If you make it hard for search engines to figure out what your pages are about, it would be normal for them to struggle to figure out how your site is relevant for users.”
For more information on how to add high-quality and useful content to category pages, check out my content tips for e-commerce websites article
Mis-Managing discontinued products
In short, discontinued product pages shouldn’t be removed automatically or on a whim.
It’s important to make sure that any discontinued product pages with value, such as if they have generated backlinks or generating substantial search traffic, are strategically managed.
Keeping the page alive with clear information regarding the likes of when the product will be back in stock alongside a range of alternative products would be amongst the best options.
For more information on this topic visit Contentkings guide on discontinued products
Relying on Supplier Content for Product Pages
It’s common for E-commerce websites to adopt a lazy approach by copying and pasting the content provided by the supplier with little or no unique content of their own.
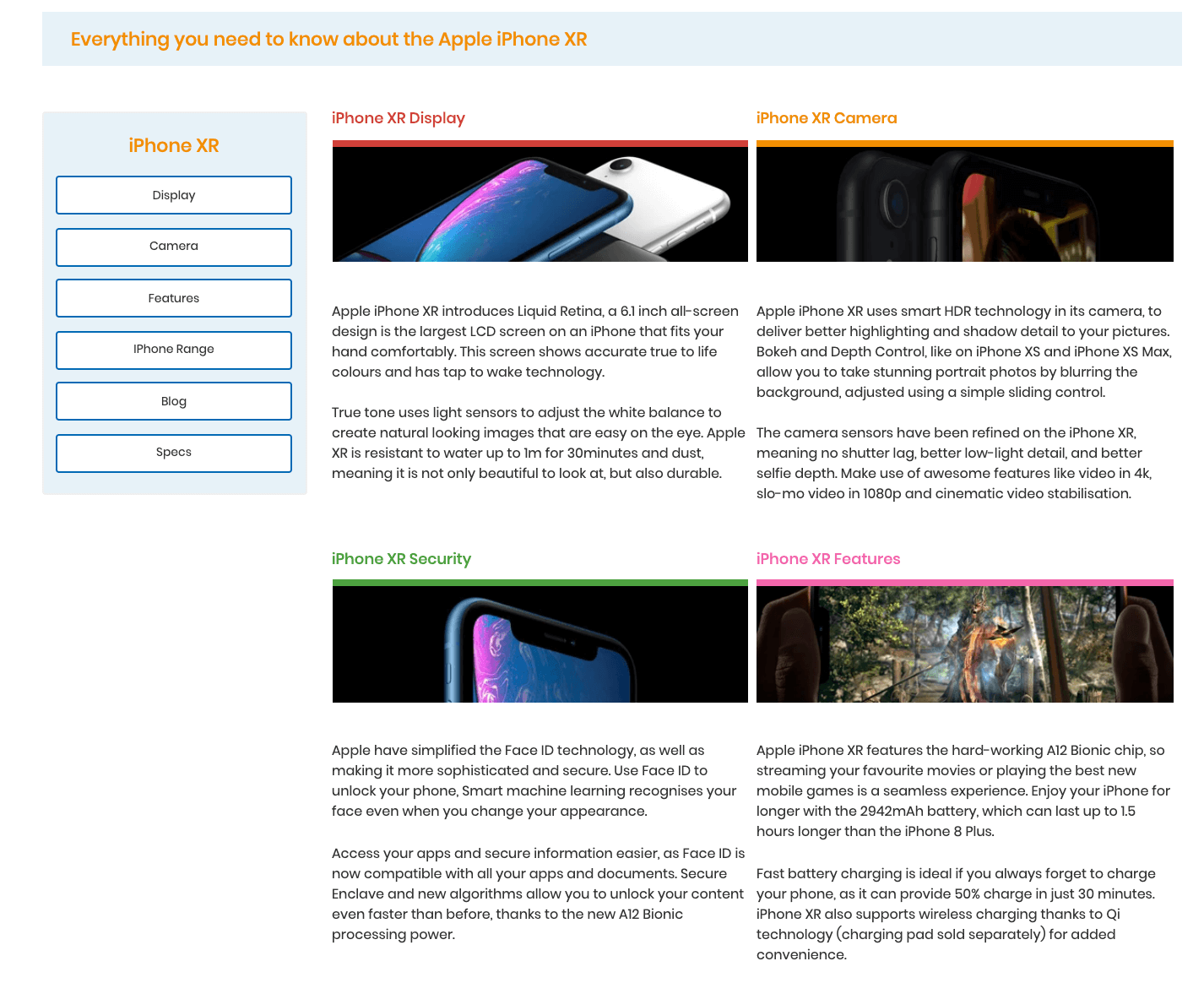
Here is an example from Vodafone, who have exclusively relied on information provided by Apple, which has been duplicated across the web, on their iPhone XR page.

Compare this to Mobiles.co.uk, who have taken the time to write unique and informative copy about the iPhone.
For any more tips and guidance on how you can improve the search visibility of your e-commerce website, get in touch with the experts at Minty Digital.